

It could have been an integer, but we'll throw it up It either as a decimal or a fraction of integers. But, for our sake, we just know that this can be representedĪs a fraction of two integers just the way that 0.3, repeating, can be. And later on, we're gonna see techniques of how do you convert this toĪ fraction of two integers. Not going to do it here, just for the sake of time, but, for example, 0.3, repeating, that's the same thing as one-third. 1313, or you have the 0.27131313, any number like this can be Now, you might not realize it yet, but any number that repeats eventually, this one does repeat eventually, you have the. This is the same thing as 0.27131313, that's what line up there represents. So, this, right over here, this would also be a rational number, but it's not an integer, Or some type of decimal that might repeat. I can't somehow make this without using a fraction Represent this any other, except as a fraction of two integers. Represented, already, as a fraction of two integers, but I don't think I can So, 0.25 is a rational number, but it's not an integerĪnd not a whole number. But there's no way to represent this except using a fraction of two integers.
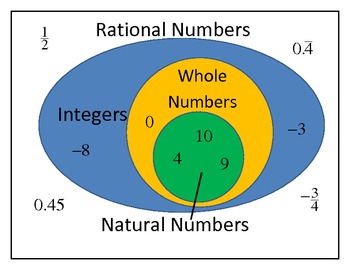
So, we can represent that as a fraction of two integers, I should say. To be a rational number, but it's not a whole numberīecause it is negative. It's an integer, and if you're an integer, you're definitely going Now, negative five, onceĪgain, it can be represented as a fraction, but it doesn't have to be, but it is negative. Number, it's an integer, and it's a rational number. You're also an integer, and you're also a rational number. It, literally, could be justĪ three, right over there, but it's also non-negative. Where would you put them on this diagram? So, let's start off with three. See if you can figure out what category these numbers fall into. These categories in place, let's categorize them. The rational numbers." All right, now that we have Just think about the rational." I'd say, "Let's think about "Let's think about the integers." But I wouldn't say, "Let's So, these are going toīe the whole numbers. So let me do that subset, right over here. The non-negative integers, you're then talking about whole numbers. So, integers are numbers that don't have to be represented as aįraction or a decimal. So, I'll do that in, let meĭo that in this blue color. And then, within rational numbers, you have integers themselves. Represented as a fraction of two integers. Infinite number of rational and an infinite number And the size of these circles don't show how large these sets are. Represented as a fraction of two integers, weĬall irrational numbers. Represented as a fraction of two integers, we call So, let's call these, or the standard way of calling these things. So this circle, over here, this represents all of the numbers that can be represented as the fraction of two integers, and, ofĬourse, the denominator can't be equal to zero,īecause we don't know what it means to put a Of number categories, and let me draw the categories. Is to see if we can classify them into different types however the digits go on infinitely but there is no pattern to them.Bunch of numbers listed up here, and my goal, in this video, π can be represented with numerals, i.e., 3.14159265. An irrational number cannot be represented as a fraction (i.e., a rational number). These expand to the real numbers ( R), which include irrational numbers such as π, √2. These can be called decimal fractions, because they can be written in a fractional form (e.g., 3/10, 32/100, ⁻27/10). We next move onto decimal numbers (such as 0.3, 0.32, ⁻2.7). Natural Numbers ( N), (also called positive integers, counting numbers, or natural numbers) They are the numbers, then other fractions (e.g., 3/4, 4/9, 7/2, 3/100, ⁻1/2 etc.) which are known as the rational numbers ( Q).

We introduce students to these gradually, and each new type comes with its own uses, and its own challenges.The main types of numbers used in school mathematics are listed below:


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
